Wooden utility poles are exposed to many different conditions along their length, from widely varying weather conditions above ground to cool damp and stable conditions deep in the ground.
It is at the ground line section of the pole where above and below ground conditions meet to create the perfect conditions for wood decay to occur.
The topsoil in the upper 6″ or so of the ground have evolved over millions of years to become a highly efficient waste disposal system. Any dead organic matter such as wood, leaves etc. that falls on the ground breaks down and is broken down by a multitude of organisms in the soil.
Fungi are very successful inhabitants of soil; they break down all kinds of organic matter, decomposing soil components. Fungi convert dead organic matter into biomass, carbon dioxide, and organic acids. There are hundreds of thousands of different types of fungi of which around 30,000 are known to attack and destroy wood. Fungal attack is the primary cause of decay and failure in wooden utility poles.
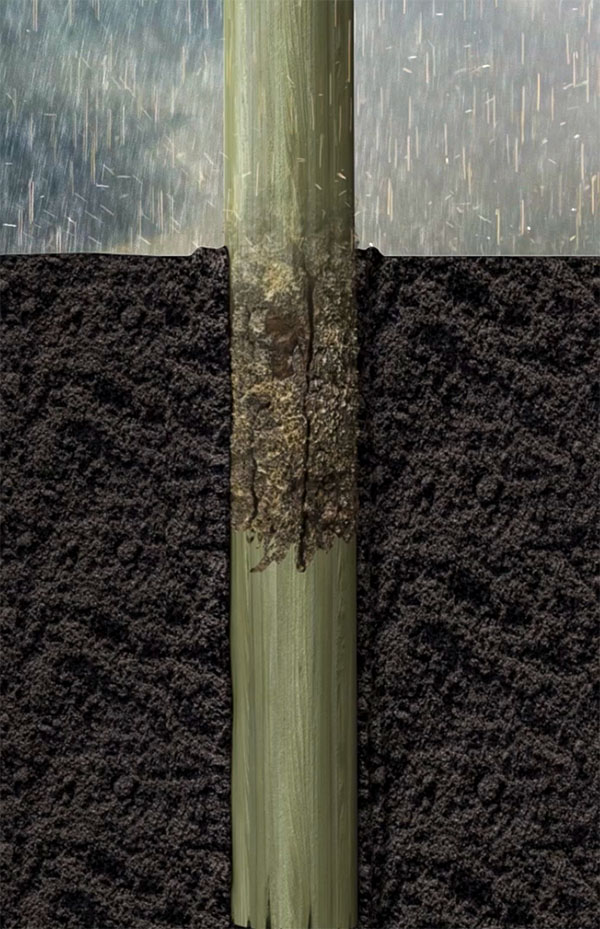

Wood destroying fungi thrive when the environment is ideal with damp, warm soil and a good supply of oxygen being essential requirements. These conditions tend to occur in the upper 150mm (6″) of the ground where rainfall, heat from the sun and a good air/oxygen supply are all present.
At greater depths, the soil tends to be more compacted, limiting the flow of air and oxygen. At the same time, the heating effect of the sun falls away, leading to lower temperatures and significantly reduced fungal activity.
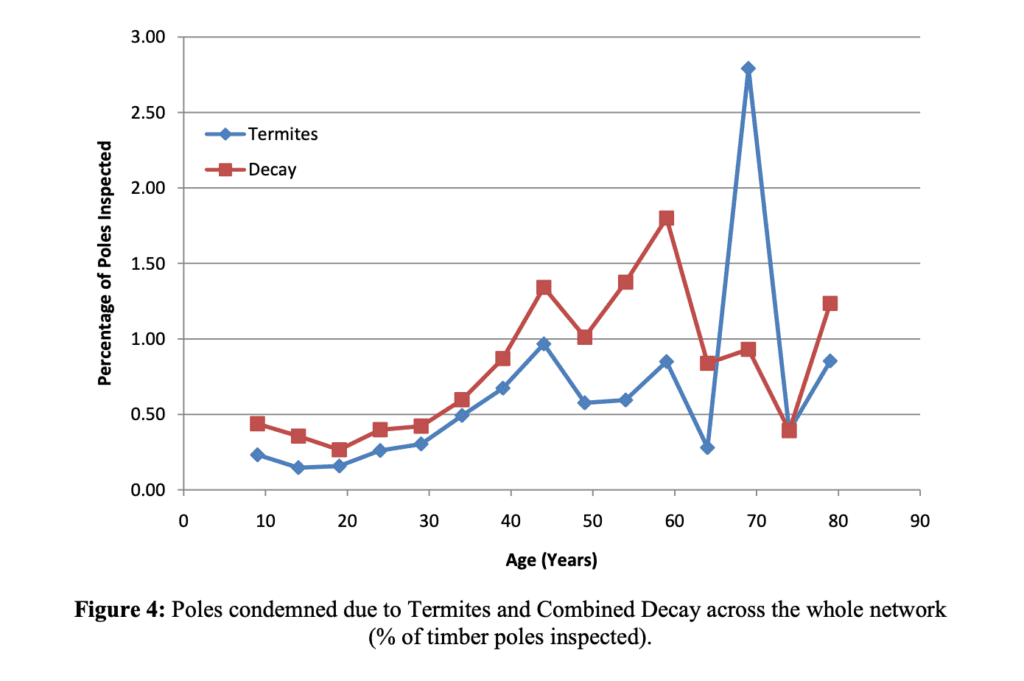
In many parts of the world, subterranean termites pose a significant threat to wooden utility poles. There are two things to bear in mind when looking at termite attack of poles. Firstly, termites don’t like eating preservative-treated wood. Secondly, as a general rule, independent research shows that many termites find it easier to digest wood that is subject to fungal decay. The graph below shows the result of large-scale testing in Australia where there is a clear relationship between the incidence of pole decay and termite attack with termite attack following shortly after the onset of wood decay. The ground line or top of the pole being the usual entry point for the termites. From this, it is clear that maintaining preservative concentrations in the wood and preventing decay is critical in reducing the likelihood of termite attack, especially at the vulnerable ground line section and to a lesser extent at the pole top.
The incidence of wood decay is directly related to the moisture content of the wood. For wood decay to start a moisture content of 25% or higher is required. If the moisture content is higher, then the rate of decay generally increases up to a point all else being equal. Once wood decay starts then it can continue at a lower moisture content of 20%, below this level wood decay does not occur.
A wooden pole buried in the ground behaves like the wick of a candle, it absorbs water from the soil with the difference in vapour pressure causing the water to move up the pole where it is lost to the air by airflow and warmth from the sun. This moisture movement is a slow but continual process with rainfall and heat from the sun being the main drivers in this process.
In practice, this generally means that the entire ground line section of the pole and the inner core of the pole section up to around 50cm or 20″ above ground will have a high moisture content greater than 25%.
You may think the section above ground will not decay as it is not in contact with fungi in the soil. Unfortunately, this is not the case; cracks in the pole form over time through to the damp core of the pole. Airborne microscopic fungal spores can be blown into the cracks and come into contact with the damp wood in the centre of the pole just above ground level. The spores can then germinate and destroy the inner core of the pole; this is called core rot.
Partial protection with liquid wood preservative applied to the pole under vacuum/pressure cycle has been the traditional method of delaying the onset of wood decay and pole failure. To be effective the preservative treatment process has to be carefully controlled to ensure correct preservative concentration (%), retention (kg/m³or PCF) level and depth of penetration (mm or inches). For best results, the pole is dried to an optimum moisture content before preservative treatment. Modern drying methods and the use of automated pressure treatment plants give consistent, high-quality protection from decay when correctly used.
The wood preservative treatment provides excellent protection above ground and deeper in the ground where conditions for decay are less than ideal. It is at the mechanically critical ground line section of the pole where wood decay and failure are an issue.
At this point exposure to higher temperatures, oxygen and moisture can accelerate the oxidation of the wood preservative. At the same time, weather changes cause regular wetting and drying cycles leading to the gradual migration of wood preservative from the pole into the soil. The overall impact is a loss of toxicity to fungal organisms over time.
Water repellent products combine biocides along with natural water repellent characteristics in the case of Creosote or the addition of oils such as AWPA P9a oil to create water repellence when used in combination with biocides such as Pentachlorophenol or copper. The oils are not “fixed” to the wood and on their own provide limited life extension as they are not biocides. They extend life by creating a partial barrier to moisture ingress from the ground*.
Over longer period of time the oil/preservatives are lost as a result of migration to the soil. This effect is most pronounced at the ground line section of the pole where climatic wetting and drying cycles combined with ideal conditions for oxidation can exacerbate this loss of effectiveness over time.
There is a European review of the licence for the continued use of creosote as a wood presevative in March 2021. With France having recently banned the use of creosote and the European Chemicals agency (ECHA) having recently classified creosote as a carcinogen, only 6 European countries now using creosote in volume it is looking increasingly unlikey that the licence for the use of creosote will be renewed.
Non water repellent water borne copper salt wood preservatives have been widely used across Europe as a more environmentally acceptable alternative to Creosote since 2005
These wood preservatives have a chequered history with reports of early pole failures but the use of additional co biocides to address the issue of copper tolerant fungi and use of fixatives, along with improved treatment standards and higher retention levels have increased pole life for newer versions of this preservative. Many of the utility customers we talk to who have used these preservatives since 2005 tell us that they expect a 15 to 20 year pole lifespan with the latest versions though longer life may be achieved in reality.
For all utilities there is a relentless focus in on cost reduction, improving safety and network reliabilty. Even with a creosote treated with 40 year pole life for most utilities wooden pole replacement is one of their single largest operating costs. In the Northern hemisphere it typically costs around €/$/£ 2500 to replace a power distribution pole and this soon adds up with a typical cost of around €/$/£25 million per 10,000 poles replaced per year.
To try and address the rising pole replacement cost issue in Europe and match the service life given by creosote, preservative manufacturers have recently launched new products that use a combination of copper-based wood preservatives and water repellent oil. This combination should undoubtedly give a longer pole life than water based copper preservative alone but how much longer is currently unknown. It is this unknown that is a concern for many utilities we speak with especiaily those who have experienced issues with pole failure in the past. Factor in feedback indicating significantly higher costs for this treatment and many of the utilities we speak to are now reviewing the options open to them including the use of alternative pole materials such as steel, composite or concrete along with partial and Total barrier systems.
An example of this is the recent decison by France Telecom (Orange) to use galvanised steel poles instead of treated wooden poles in France, in spite of this increasing their CO2 emmisions by around 220,000 tonnes a year. This is bad for the environment and a major blow to the wooden pole producers, forestry sector and preservative manufacturers with lost sales of around 220,000 poles a year.
* Full reports available on request

The costs to a utility to install and maintain wooden utility poles is often one of their single highest expenditures. Using annualised combined costing that includes installed cost and inspection and remediation costs spread over the poles expected life gives a clear and easy to use figure for pole cost, and comparison against alternatives.
Let’s take a 1000 mile North American LV distribution network as an example; our research based on industry data shows:
– with an average pole spacing of 250ft equating to 21,120 poles, the combined costs of each pole and the cost of installation totals $63 million.
– Based on the assumption that 12% of these poles are inspected every ten years at an inspection cost of $100, annual pole maintenance cost would be $633,000 including remediation work.
– Based on a 20-year lifespan for a water-based copper preservative (Creosote/CCA 40 years), the total lifetime maintenance cost for 21,120 poles would be $25 million.
– In total, the lifetime cost of 21,120 poles, based on our industry research data, is $88 million.
Our data shows that the maintenance costs to Utilities are substantial. Although this example is specific to North America, our research has expressed similar results across a range of geographical locations.
In conjunction with the apparent costs, several potential hidden costs can occur as a result of pole failure. Depending on market regulation, grid failure as a result of pole collapse may incur financial penalties for Utilities. Pole collapse not only has the potential to cause grid failure, but it also presents a possibility for compromising the safety of employees and the public. The likelihood of these failures and the resulting costs can both be reduced; if you would like to know how much you could save with polesaver try our cost calculator for more information.
These unwanted costs, both explicit and hidden, are a significant target for potential reduction. Look out for our next article as we explore the available alternatives for prolonging pole life, including alternative pole materials and partial and full barrier systems and their effects on maintenance, safety and the environment.



This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.